In this first chapter, we are going to find the answer to the question what is living? After completion of this chapter, you should be able to tell the characteristics which separate living things from nonliving things. To learn this chapter via video lecture, click the lecture tab below.
[tabby title=”Material”]
What is living?
Many diverse forms of the living organism are found on earth in different types of habitats such as river, ocean, hot water spring, mountains, forests, etc.
What is living? It is extremely hard to characterize “living” and traditionally different qualities common to every single living being are to be recognized. Some of the important characteristics of living are Cellular Association, Growth, Reproduction, Metabolism, and Consciousness/homeostasis. Apart from these, there are characteristics like respiration, excretion, cell division, stimulation response, etc.
Cellular Association
Living things are composed of a single cell (otherwise called as unicellular organisms) or many cells (otherwise called as multicellular organisms) which associate with each other to perform vital functions of the body.
Growth
Growth means an increase in number through cell division and increase in weight. In plants, cell division occurs only up to a certain age. However, in animals, the cell division occurs in certain tissues to replace lost cells. But we should remember that non-living objects will also grow in the sense of an increase in body mass. For example mountain growth. This is due to accumulation of material on the surface. But in living organisms, the material on the surface. But in living organisms growth is from inside. Therefore, we cannot consider growth is from inside. So, we cannot consider growth is the defining property of living organisms.
Reproduction
All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is by both asexual and sexual method.
Asexual reproduction occurs in different ways such as – binary fission (occurs in amoeba, bacteria), Budding, (occurs in yeast and hydra), Fragmentation (occurs in filamentous algae), Regeneration (occurs in plants), Vegetative propagation (occurs through stem, root, leaf and bulbil of plants), Sporulation which occurs in spore, algae, fungi.
Sexual reproduction is a form of reproduction where two morphological different types of female ovum and a male sperm work together to produce an offspring. When two gametes fuse together single-celled zygote is formed. Sexual reproduction occurs through Gamete formation, gamete transfer, gamete fusion/fertilization and embryogenesis.
Metabolism
Metabolism is another characteristic feature of living; The chemicals, which may be small and big belonging to various classes, functions, and sizes are continuously being made and changed into other biomolecules. These chemical reactions are called as metabolic reactions. The sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in living organisms body is metabolism. Isolated metabolic reactions in vitro are not living things. Cellular organization of the body is the defining feature of life forms. The biochemical reaction in living is by both constructive and destructive manner.
Anabolism is a constructive biochemical reaction which refers to the process which builds molecules the body needs; it usually requires energy for completion of the reaction. Catabolism is a destructive biochemical reaction which refers to the process of breaking down of the complex molecules into smaller molecules; it usually releases energy for the organism to use.
Consciousness
It is the complicated feature of all living organisms. It is the ability to sense their surroundings or environmental stimuli which could be physical, chemical or biological. Sense organ in the organisms helps in sensing the environment. Plants are responding to light, water, temperature, other organisms, and pollutants. Such a way all organisms from prokaryotes to the most complex eukaryotes responding to the environment. Therefore, consciousness becomes the defining property of living organisms. But in the case of brain dead condition in organisms will not have self-consciousness. In such condition, it is difficult to define living or nonliving.
[tabby title=”Lecture”]
Audio Transcript of What is Living Video
0:05 – In this video, we will discuss the basic characteristics of the living organisms. Sometimes it is very much difficult to decide whether an organism is living or nonliving. There are some basic characteristics on the basis of which we can differentiate living and the non-living organisms. Let us discuss what are those characteristics, one by one.
0:30 – First of all we will discuss Homeostasis which is defined as the maintenance of the internal temperature or the maintenance of the internal environment of the body. Those organisms can maintain their internal environment or internal temperature of the body are termed as living organisms maintaining the internal temperature.
1:00 – The second characteristics on which we can differentiate living and non-living organisms are organization. Organization means whether an organism is made up of a single cell or multiple cells. Example of Single-cell organism is amoeba and multiple cell organisms are humans or animals.
2:00 – The major characteristic on which we can differentiate is metabolism. Metabolism is of two kinds. Anabolism and Catabolism. Anabolism is defined as a complex process, it is the synthesis of complex molecules. Secondly, the processes of catabolism which are defined as the breakdown of the larger molecules into the smaller molecules like polysaccharide into the monosaccharide proteins into the amino acids nucleic acids into the nuclear nucleotides, etc. Catabolism is defined as the breakdown of larger molecules or complex molecules into the smaller ones which are necessary for the sustaining of life.
4:40 – We will discuss the next characteristic which is growth. Growth is one of the fundamental process involved in the life processes of a living organism. The next process is of adaptation. Adaptation is the process by which an organism inherent itself to the environment in which he is living whether the conditions are suitable or not. The organism will adapt to that environment in which he has to survive.
5:10 – After discussing all these processes, the next process is the response to stimuli. What is a stimulus? Stimulus is any kind of external foreign material to which our body responds. This response may be active or passive. Active means direct and passive always used to occur in inorganic substances or nonliving substances.
6:10 – The next most important criteria or the characteristic for describing living organism is the reproduction. Reproduction is one of the major life forms to sustain life. It is the production of fertile offspring. After understanding and following all these basic characteristics we came to know that what are those characteristics on the basis of which we can differentiate our living and our nonliving substances. In this video, we learned about the basic characteristics which are involved in the differentiating living and non-living. In our next video, we will discuss biodiversity.
[tabby title=”Revise”]
Concepts in What is living Chapter
Mnemonics
Seven characteristics of all living organisms
Differences
Anabolism and Catabolism
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
Questions


Browse All Questions from this chapter
[tabby title=”Beginners”]
Before we talk about what is living, let us first see what is biology?. Biology is the story of life on earth. It is a science which deals with the study of living organisms. Biology is derived from Greek Words Bio (Life) + Logy (the study of). The major divisions of biology are Botany ( the study of plants) and Zoology (the study of animals). The scientific study of physiology, structure, genetics, classification of plants is called Botany and scientific study of physiology, structure, genetics, classification of animals and human is called Zoology.
What is Living?
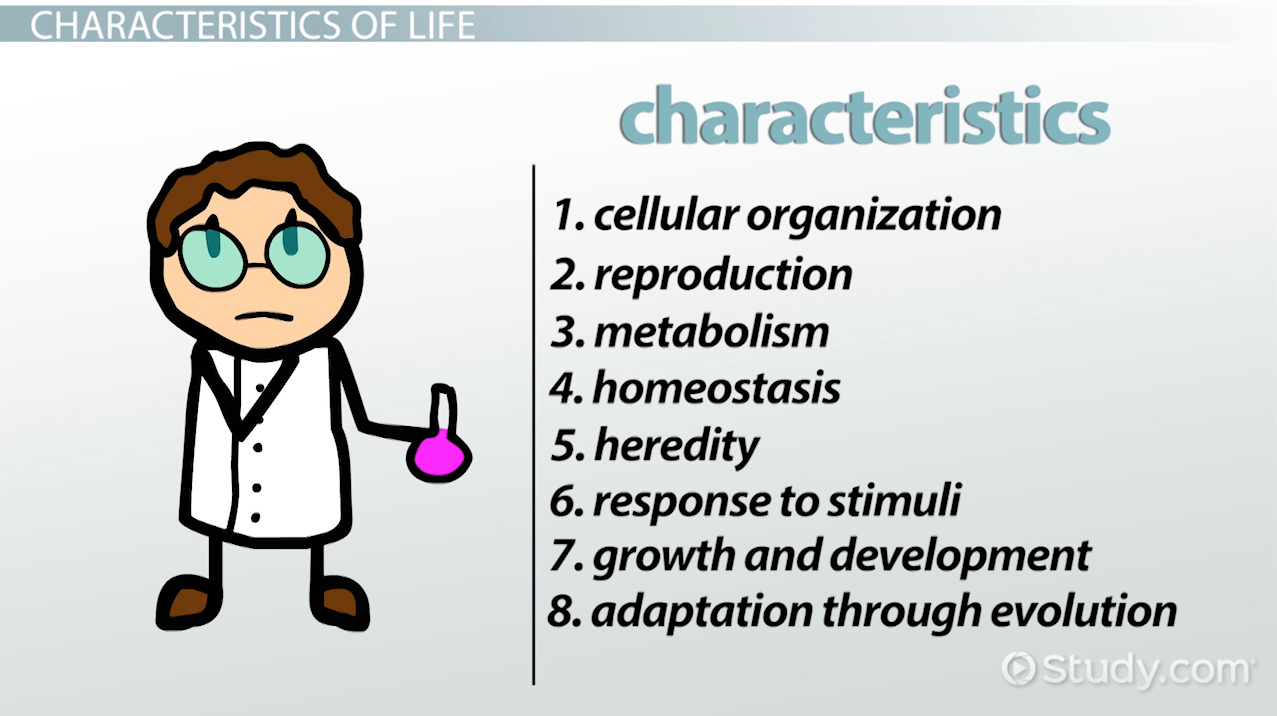
There are 7 characteristics which mainly differentiate living organisms from non-living things. These fundamental characteristics of living organisms are growth, reproduction, metabolism, excretion, movement, sensitivity, respiration and nutrition. Growth and Reproduction are not the only defining factor for living organism but metabolism, sensitivity, and cellular organization are defining characteristics of living organisms. In this chapter, we are going to explore each of these characteristics in detail.
Growth :
The twin characteristics of growth are the increase of mass of the organism and multiplication of organisms (reproduction). All multicellular organisms grow by cell division. Cell Division is the process in which the parent cell divides into two are more daughter cells. For unicellular organisms, cell division creates an entire new organism (reproduction). For multicellular organisms, cell division results in an increase in mass of the organism.
Cell Division occurs throughout the lifespan of plants whereas cell division stops after a certain age in case of animals. Cell Division in animals is not completely stopped but the rate of division decreases and occurs only in certain tissues to replace the lost cells.
The increase in the mass of the organism is not the only factor which determines the growth process. Some non-living objects such as sand beds also grow because of accumulation of more sand on the surface. This kind of growth, which happens from outside in non-living things is not considered as growth. In the case of living organisms, the growth happens from the inside.
Cell Division does not occur in the dead organism and so it does not grow.
Reproduction:
All non-living objects do not have the capability to reproduce or replicate itself. It is possible only for the living organisms. In the case of single cell organisms like bacteria or amoeba, there is no difference between growth and reproduction. For these unicell organisms, reproduction means an increase in the number of cells as in the case of growth, In the case of multi-cell organism, reproduction refers to the capability of the organism to produce the replication of the self.
Not all organisms reproduce by sexual reproduction, some organisms such as Fungi reproduce asexually. Any reproductive unit that is capable of giving rise to a new organism without sexual fusion is called Spore. Algae, Fungi, and Protozoans are spores.
In small organisms such as yeast and hydra, asexual reproduction occurs by the process of budding. Budding is a type of asexual reproduction where a small part of the body of the parent organism grows out of a small project, a bud which detaches to develop into a new organism.
In the case of flatworms (Planaria), reproduction occurs through fragmentation. Fragmentation is the process by which a new organism grows from a fragment of the parent and develops into a fully grown organism by regenerating the missing parts.
Although there is no non-living object which is capable of reproduction, it is not the only characteristic which separates living organisms and non-living objects because there are many organisms such as mules, sterile, worker bees, and infertile human couples.
Metabolism:
All living organisms are made up of chemicals. These chemicals react with one another throughout the life cycle of the organism. In the case of both unicellular and multicellular organisms, thousands of chemical reactions (also called metabolic reactions) occur simultaneously in the body of the organism. The sum total of all chemical reactions that occur in the body of the organism is called the metabolism.
The chemical reactions we conduct in chemistry labs using test tubes which mimic the metabolic reactions (which happen inside the body) is neither living nor non-living. The three main purposes of metabolism are the conversion of food to energy, the conversion of food to building blocks for carbohydrates and proteins, and the elimination of wastes from the body. These metabolic reactions allow organisms to grow and respond to their environments.
Cell Organization:
The cell is the basic building block of all living organisms. Non-living objects do not have cells. The other characteristics of living organisms such as growth, reproduction, and metabolic reactions happen at the cell level.
Homeostasis
The conditions inside the body must stay relatively constant irrespective of change in the environment. An organism maintains a stable environment inside to survive. This maintenance is called as homeostasis. When the body gets cold, it gives shivering to indicate you to move to the hotter place to maintain the internal temperature.
Sensitivity / Consciousness
All organisms are aware of their surroundings. They have the ability to sense the environment using the sensory organs and respond to the physical, chemical or biological stimuli. Plants respond to environmental factors such as temperature, water, pollutants in air, light, water, etc. The most common example for plants and animals are the photoperiod(the time which the organism receives daylight) that affects reproduction in seasonal breeders. This ability to sense surroundings is called as consciousness.
The human being apart from having awareness about the surroundings also has the awareness about the self (self-consciousness). When it comes to human beings, it is much more difficult to say that consciousness is the only determining characteristic of living beings as there are patients who are lying in the coma for years without self-consciousness.
[tabbyending]
Subject: Biology (4253)
Important MCQs Based on Medical Entrance Examinations To Improve Your NEET Score
18000+ students are using NEETLab to improve their score. What about you?
Solve Previous Year MCQs, Mock Tests, Topicwise Practice Tests, Identify Weak Topics, Formula Flash cards and much more is available in NEETLab Android App to improve your NEET score.
Share this page with your friends

Leave a Reply